- Products
- New Products
- Featured Products
- Color and Print Themes
- Blood Pressure Measurement
- NIBP / Vital Sign Monitors
- Digital Aneroid Sphygmomanometers
- Palm Aneroid Sphygmomanometers
- Pocket Aneroid Sphygmomanometers
- Pro's Combo Sphygmomanometers
- Multicuff Sphygmomanometers
- Clock Aneroid Sphygmomanometers
- Mercury Sphygmomanometers
- Home Blood Pressure Measurement
- Adcuff +
- Gauges
- Bulb & Valves
- Disposable Cuffs
- Reusable Cuffs & Bladders
- Sphygmomanometer Accessories
- Sphygmomanometer Parts
- Caseware
- CPR / Airway
- EENT
- Instruments & Accessories
- Laryngoscopes
- Penlights
- Pulse Oximeters
- Stethoscopes
- Thermometry
- Vital Signs Monitors
- Solutions
- About ADC
- Learning Center
- Support
- Blog
- Contact
Adjustable Frequency Diaphragms: Fine Tuning for Better Auscultation
Written By:
The ADC Medical Education Team
Posted On:
October 04, 2023
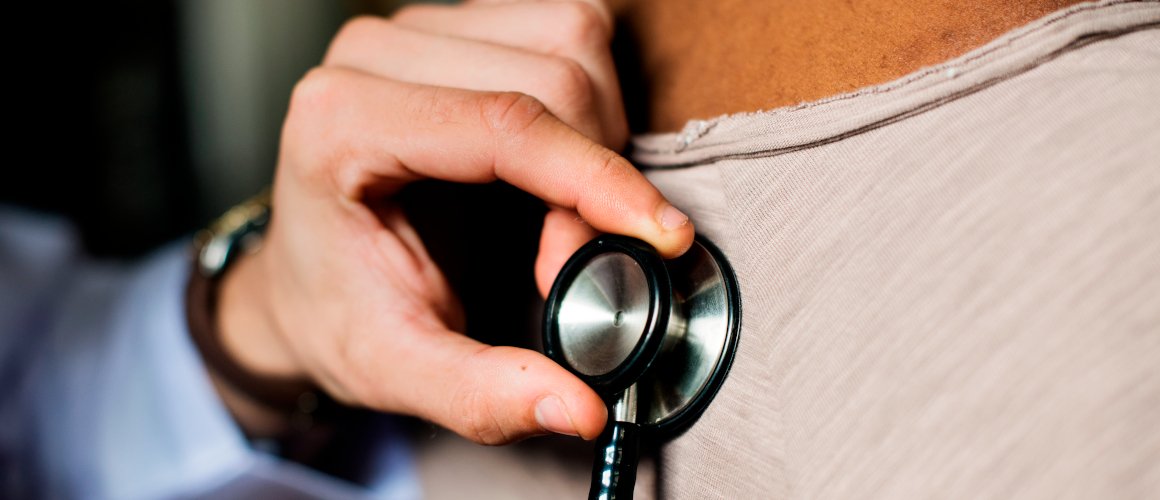
The stethoscope is an iconic instrument. It allows you to tune in to the intricate symphony of bodily sounds, from the rhythmic thumping of the heart to the gentle melody of breath sounds. Understanding how the diaphragm side of a stethoscope works to capture breath sounds is essential for healthcare professionals and can greatly impact your ability to diagnose and treat patients effectively.
Breath sounds provide valuable insights into a patient's respiratory health, revealing clues about lung function, the presence of infections, and other pulmonary conditions. To comprehend how the diaphragm side of a stethoscope plays a crucial role in this, one must first understand the characteristics of breath sounds.
What Are Breath Sounds?
Breath sounds are the acoustic manifestations of the air moving in and out of the respiratory tract. These sounds possess unique characteristics that differentiate them from other bodily sounds, such as heartbeats. One notable distinction is their pitch. Breath sounds tend to be higher pitched compared to the lower, rhythmic thuds of the heart.
The variance in pitch is primarily due to the difference in the source of these sounds. While heart sounds originate from the closure of heart valves and the blood's movement through the chambers, breath sounds arise from the turbulent flow of air through the airways. This turbulence generates the distinctive higher-frequency vibrations that you listen for during auscultation.
The Diaphragm Side: Tuned to the Music of Breathing
The diaphragm side of a stethoscope is the key to capturing these intricate breath sounds. It consists of a flat, circular membrane, usually made of high-quality materials like rubber or plastic, attached to the chestpiece with a retaining rim. When placed against the patient's skin, the diaphragm collects and directs sound.
Adjustable Diaphragms: Improving Diagnostic Range
One significant advancement in stethoscope design is the incorporation of adjustable diaphragms. These diaphragms can be tuned to better capture both lower- and higher-frequency sounds, simply by applying more or less pressure against the patient’s body.
Stethoscopes with adjustable diaphragms offer several advantages that can enhance the accuracy of patient assessments:
- Enhanced Frequency Ranges: Fine-tuning the diaphragm to higher frequencies makes it easier to discern subtle changes in breath sounds, like wheezing, crackles, or shallowness, all of which can be critical indicators of lung health. This is particularly valuable in diagnosing respiratory conditions like asthma or pneumonia.
- Versatility: Stethoscopes with adjustable diaphragms are more versatile. For a single-sided chestpiece, adjustable diaphragms provide a wider overall acoustic range. But even dual-headed instruments with a dedicated bell side for lower sounds can benefit, since you can still pick up lower sounds using the diaphragm, eliminating the need to flip the active chestpiece side in the middle of an exam.
- Reduced Ambient Noise: The ability to focus on specific frequency ranges also helps reduce interference from ambient noise in clinical settings.
Did you know that Adjustable Frequency Design (AFD) diaphragm technology is standard on nearly every ADC Adscope Clinician and Cardiology stethoscope? And with Free Parts Forever, you’ll get complimentary replacement diaphragms for the life of your instrument!
